Have you ever wondered “are sweet potatoes good for diabetes?” Here is my dietitian insight and key things to consider.
There’s a lot of confusion around sweet potatoes and if they can be included in a diabetes-friendly diet. So, let’s take a look and determine, “Are sweet potatoes good for diabetes?”
Can people with diabetes eat sweet potatoes?
Yes! Just like most other foods, people with diabetes can eat sweet potatoes. But, because they are higher in carbohydrate than other vegetables, enjoying them without a blood sugar spike can often require a little more planning and thinking ahead.
We’ll cover the many different ways sweet potatoes can be enjoyed while living with diabetes below. My favorite simple way to enjoy them (as someone living with diabetes myself) is from the microwave actually. They come out super soft. I pair it with a non-starchy veggie and some air fried salmon!
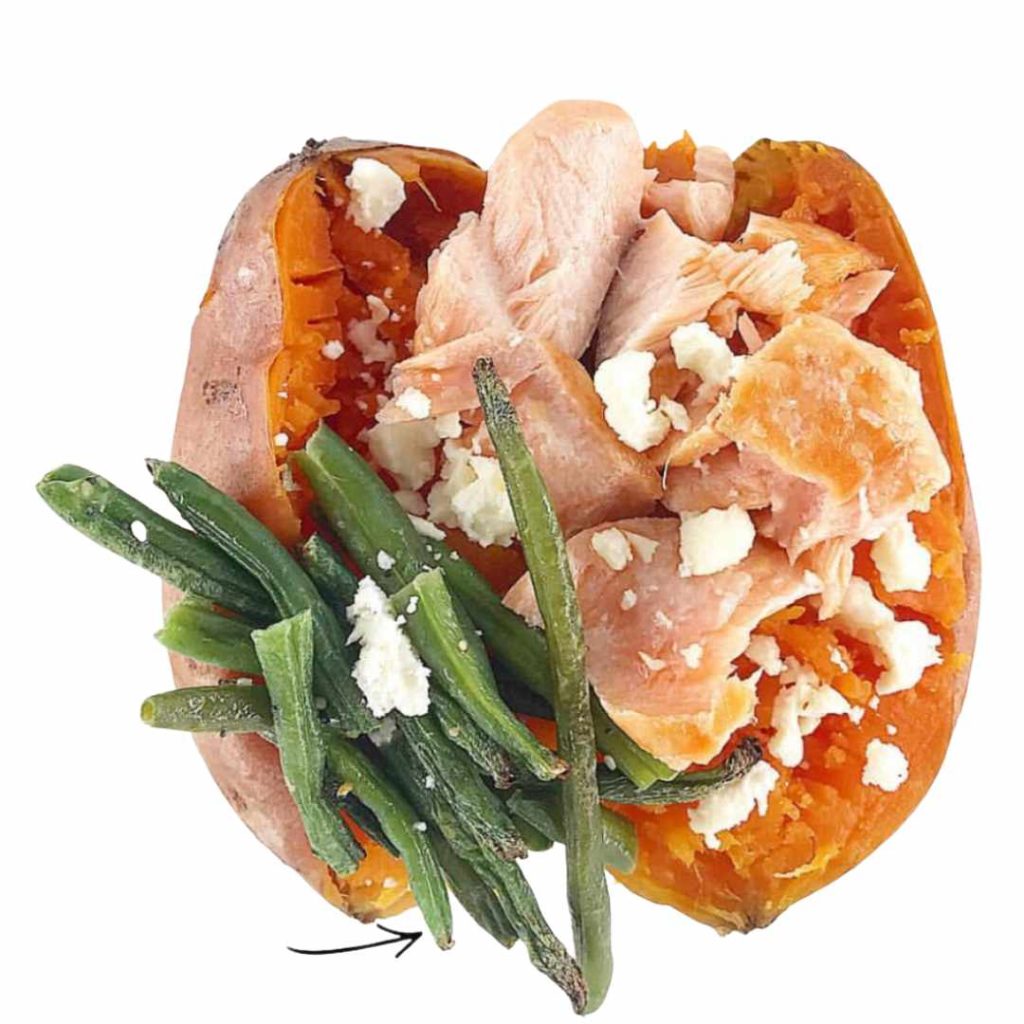

Nutrition benefits of sweet potatoes
When you hear the words “sweet potato”, most people think of the beautiful orange colored potatoes we all know and love. But, did you know they can also come in white, yellow, red/purple, and dark purple colors too?
Sweet potatoes are actually an edible root. (Unlike white potatoes which are edible tubers.) They are rich in:
- Vitamin A (beta carotene)
- Vitamin B6
- Vitamin C
- potassium
- fiber
Orange sweet potatoes contain more beta carotene, while purple sweet potatoes contain more anthocyanins. Both beta carotene and anthocyanins, are health promoting antioxidants.
How many carbs are in a sweet potato?
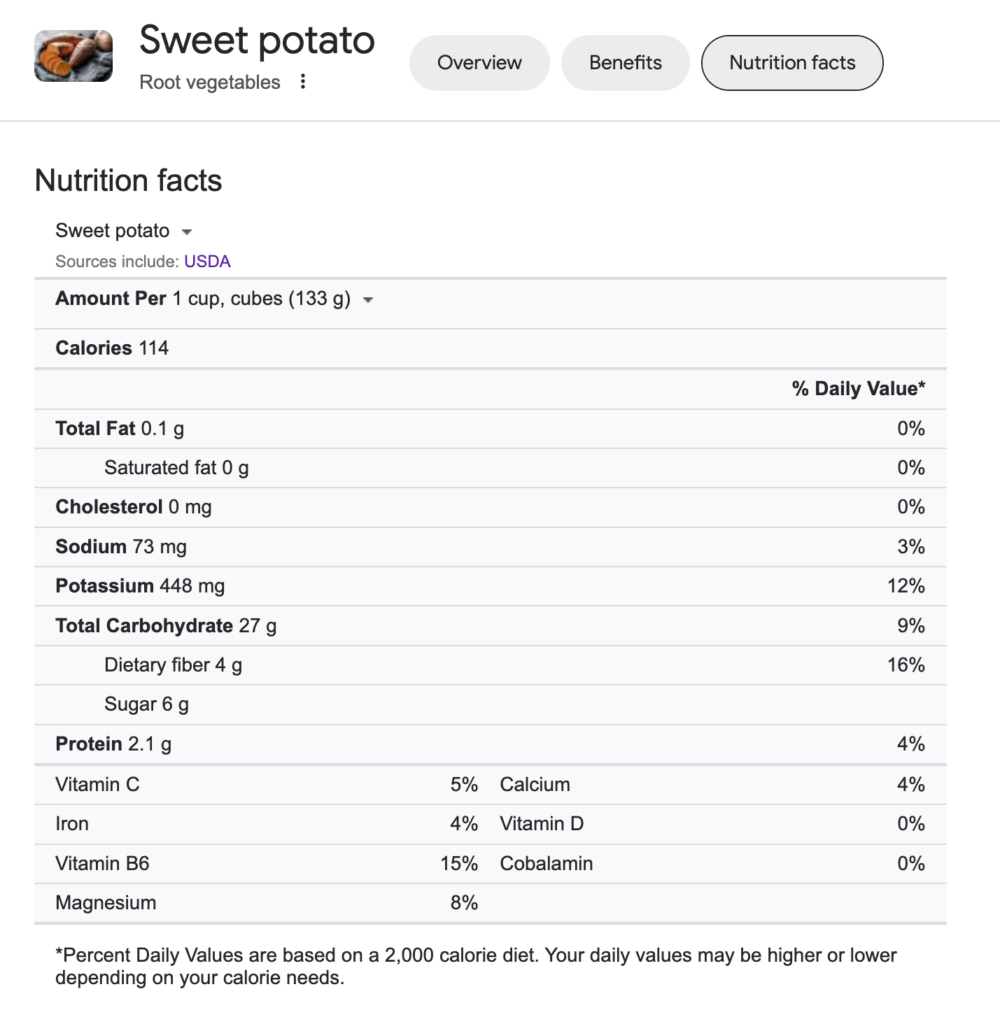
Are sweet potatoes high in carbs? Honestly, the answer is yes and no. It depends on the size of the sweet potato. A small sweet potato (about 5in long) or 1 cup of cubed sweet potato contains about 26g carbohydrate.
How much sugar is in a sweet potato?
Within the carbohydrates mentioned above, sweet potatoes contain 6g sugar and 4g fiber.
Can sweet potatoes increase blood sugar?
Yes, just like other foods that contain carbohydrates, sweet potatoes can raise blood sugar levels. How quickly and how much they can raise blood sugar levels will depend on the amount eaten.
Sweet potato glycemic index
The glycemic index tells us how quickly a food can raise blood glucose levels. (It does not take into account how much carbohydrate is in a food.) The glycemic index of sweet potatoes varies depending on how they are prepared though. This is because of the preservation (or not) of resistant starch depending on the cooking method. Sweet potatoes can be a low, moderate, or high glycemic index food.
| Low glycemic food | 0-55 |
| Medium glycemic food | 56-70 |
| High glycemic food | >70 |
| Cooking method for sweet potatoes | Glycemic Index value | Glycemic Index category |
| Boiled 8 minutes | 61 | Moderate |
| Boiled 30 minutes | 46 | Low |
| Roasted and peeled | 82 | High |
| Baked 45 minutes (peeled) | 94 | High |
| Fried | 76 | High |
Sweet potato glycemic load
The glycemic load, however, can be a more accurate picture of how much and how quickly a food may raise blood sugar levels. The glycemic load considers both how quickly a food can raise blood sugar levels and how much carbohydrate is in the food. This tells us how much of an impact a food can potentially have on blood sugar levels. The glycemic load of sweet potatoes is 11.1.
| Low glycemic load | 0-10 |
| Moderate glycemic load | 11-19 |
| High glycemic load | 20+ |
Sweet potatoes are considered a moderate glycemic load food. Low and moderate glycemic load foods are considered more beneficial for people looking to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Is sweet potato good for diabetes?
Are sweet potatoes bad for diabetes? Are they good for diabetes? While no food or part of nutrition is ever as black and white as being good or bad, just remember that if you like sweet potatoes, you can absolutely enjoy them while living with diabetes. The most important parts if enjoying them to pay attention to are the serving size, overall carb count, and what you’re eating them with.
Is sweet potato good for type 2 diabetes?
Yes, whether you’re managing type 1, type 2, or gestational diabetes, sweet potatoes can be a good blood sugar friendly addition to your meals.
How to cook potatoes for diabetes
As we’ve mentioned above, there are many different ways you can cook a sweet potato. But, it seems that boiling sweet potatoes with the skin on is the best option for maintaining nutrient content. This includes beta carotene, vitamin C and resistant starch.
And, because microwave cooking is considered a “wet” cooking method, we can assume that when we cook a sweet potato in the microwave, nutrient retention would be more similar to boiling than roasting.
What to eat with sweet potatoes
I recommend pairing sweet potatoes with your favorite non-starchy vegetables and protein sources. These types of foods can help reduce the potential impact on blood sugar levels as well as possible blood sugar spikes.
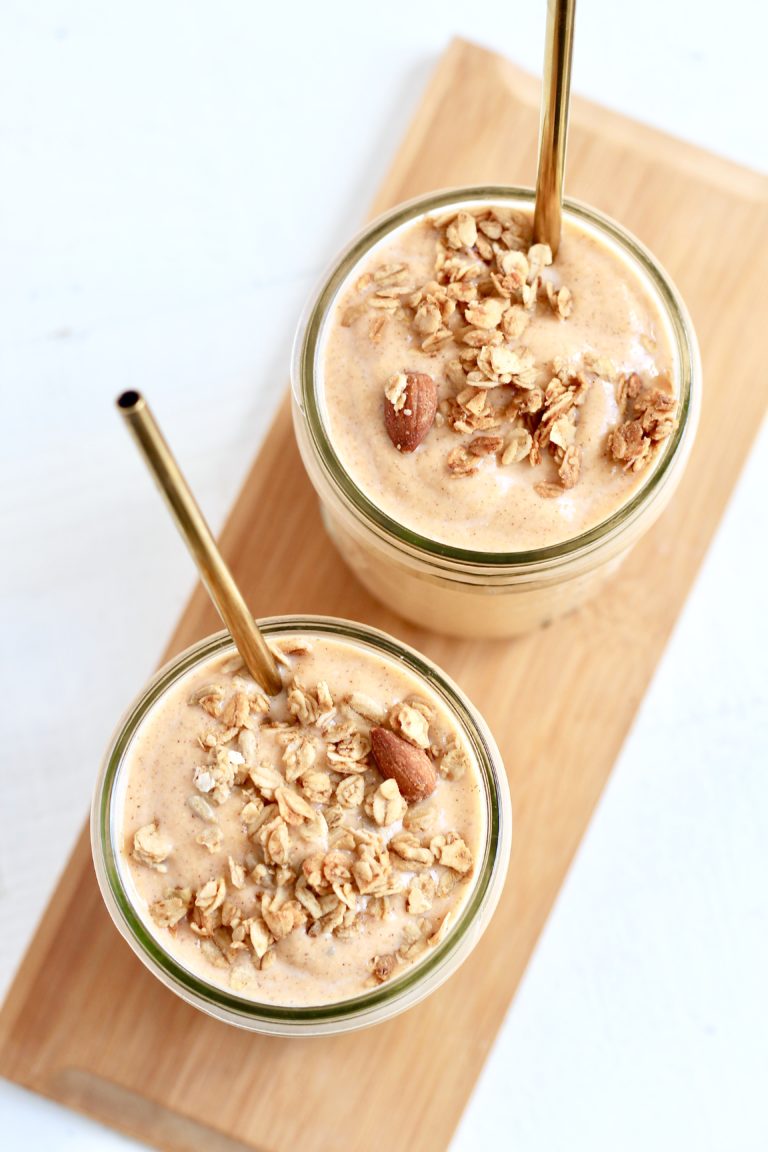
Creamy Sweet Potato Kefir Smoothie
This recipe uses the lowest glycemic form of cooked sweet potatoes: boiled sweet potatoes!

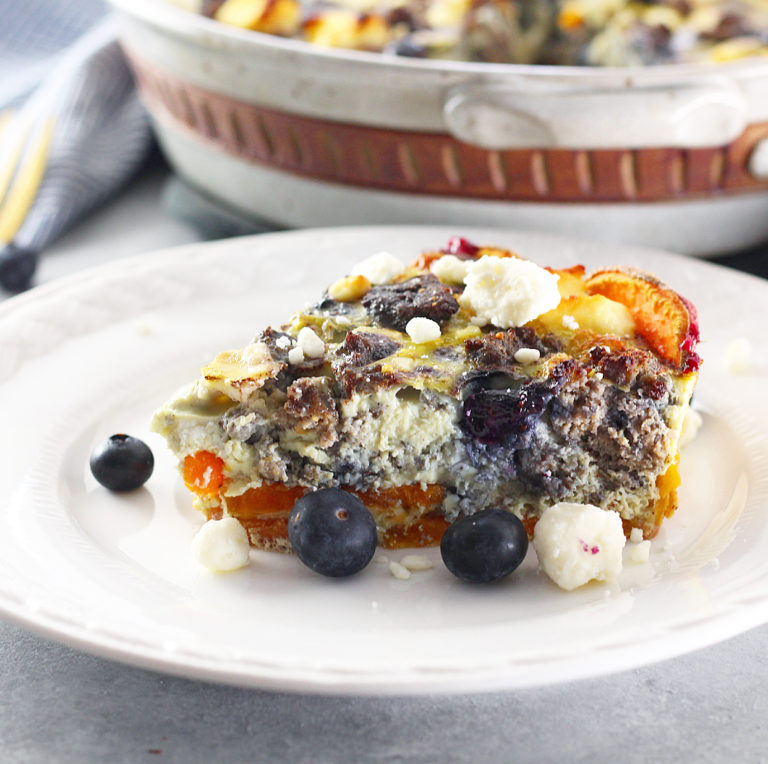
Sweet Potato Blueberry Sausage Frittata
This recipe adds in other sources of fiber and protein for a balanced sweet potato loving meal!

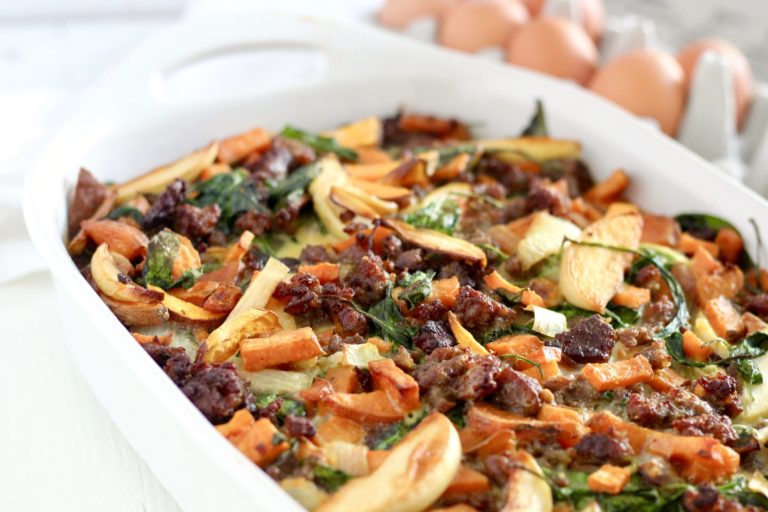
Sweet Potato Overnight Breakfast Bake
This casserole is one of my favorite make ahead breakfast options!

Sweet potatoes and diabetes: The final word
Sweet potatoes can be a delicious part of a diabetes-friendly diet. Yes, they do contain natural sugar and carbohydrates, but they also contain fiber and health promoting antioxidants. Prepare them with the skin on and be mindful of your serving size. You can enjoy them on their own or added to your favorite dishes!
What other foods are good for diabetes?
- Is oatmeal good for diabetes?
- Are beets good for diabetes?
- Is peanut butter good for diabetes?
- Is pineapple good for diabetes?